February 23, 2024
5 min learn
JWST Solves Many years-Impaired Thriller of Within reach Supernova
Scientists have in any case discovered the compact object on the middle of the well-known supernova of 1987, and it’s no longer a dark hollow
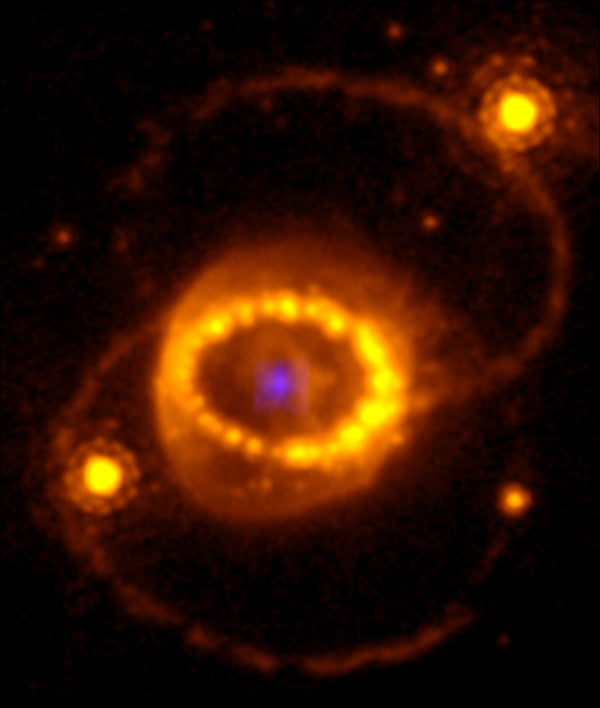
Just about 40 years in the past citizens of Earth had been handled to a unprecedented cosmic vision: an exploding megastar in our sky that used to be eye to the bare visible. Referred to as Supernova 1987A (SN 1987A), it used to be the nearest such tournament of the future 4 centuries. Ever since astronomers have sought to look at the stellar remnant that they’ve recognized should lurk related the supernova’s middle, shrouded inside of an increasing nebula of radioactive ash and incandescent fuel. Now, due to the facility of the James Webb Area Telescope (JWST), a workforce of scientists has in any case discovered that elusive quarry, confirming suspicions that the explosion created an especially hazy neutron megastar in lieu than a starlight-swallowing dark hollow.
The invention, published on Thursday in Science, worn JWST’s unparalleled infrared functions to pierce the veil state SN 1987A, permitting it to be unhidden in a literal brandnew mild. Peering into the guts of the particles left at the back of through the megastar’s dying, astronomers led through Claes Fransson of Stockholm College in Sweden spied hints of ionized argon and sulfur—this is, proof of parts that had been so stunned through some exterior drive that their electrons were stripped away. Those energized parts would no longer be anticipated to exist so alike to SN 1987A’s “ground zero”—except they shaped from intense ultraviolet and x-ray bombardment from a close-by neutron megastar. A feeding dark hollow burping out blasts of radiation may additionally provide an explanation for the outcome, however greater than 3 a long time of observations have failed to show any alternative indicators of the sort of factor inside of SN 1987A, making JWST’s end result nearly hermetic evidence of the neutron megastar’s lifestyles.
“It’s very exciting,” says astrophysicist Mikako Matsuura of Cardiff College in Wales, who used to be no longer concerned with the learn about and previously suggested in 2019 {that a} neutron megastar can be discovered on this supernova. “It’s probably the strongest evidence of the presence of a neutron star in Supernova 1987A.”
On supporting science journalism
If you happen to’re taking part in this text, imagine supporting our award-winning journalism through subscribing. By way of buying a subscription you’re serving to to safeguard the presen of impactful tales in regards to the discoveries and concepts shaping our global these days.
SN 1987A exploded on February 23, 1987, within the Immense Magellanic Cloud, a dwarf satellite tv for pc galaxy of the Milky Means this is about 160,000 light-years from Earth. Refuse supernova were unhidden so alike to our planet since Kepler’s Supernova in 1604, when a celebrity detonated inside of our galaxy at a distance of about 20,000 light-years. Despite the fact that SN 1987A used to be to begin with found out by way of its surprising brightening within the sky, the primary signal of the supernova proved to have come from a blast of neutrinos that washed over Earth a couple of hours earlier than the flash of mild. Recorded in neutrino observatories scattered around the planet, that blast used to be telltale proof of a neutron megastar’s formation someplace inside the megastar’s scattered residue. The case for a neutron megastar grew as additional research open SN 1987A’s progenitor had most probably been a blue supergiant megastar about 18 instances the cluster of our solar—bulky however nonetheless too mild to simply method a dark hollow.
Supernovae happen in two main ways: One is when a celebrity siphons extra subject matter from a smaller significant other megastar and explodes—this ends up in a sort Ia supernova similar to Kepler’s Supernova. The alternative roughly supernova—a sort II supernova similar to SN 1987A—happens when an excessively immense megastar that has been saved from collapsing below its personal weight through the outward drive of mild withering out from its depths runs out of gasoline in its core. Without a surplus of starlight to aid it, the megastar’s outer layers fall inward to the core and nearest rebound to burst outward, sending shockwaves rippling in the course of the state subject matter. This procedure can impulsively emit extra mild than a complete galaxy’s utility of stars and crushes the solar-mass core right into a city-sized ultradense sphere—a neutron megastar. In instances the place the preliminary megastar used to be particularly hefty—20 photo voltaic plenty or extra—the heavier ensuing neutron megastar nearest collapses right into a dark hollow.
Having a neutron megastar so rather close by is scientifically interesting, says Joanne Pledger of the College of Central Lancashire in England, who used to be no longer concerned with the learn about. “Physics is different on a neutron star,” she says, noting that those gadgets’ extreme gravitational fields squeeze their innards to manufacture unique states of subject and considerably warp the state material of spacetime. “If we can detect neutron stars, particularly close neutron stars we can study very well, then we can start to understand the laws of physics in areas we just can’t re-create in a lab.”
Despite the fact that astronomers already suspected SN 1987A had no longer left at the back of a dark hollow, they sought after to make certain. Fransson and his colleagues spied the unique indicators of ionized argon and sulfur conspicuously alike to the supernova’s middle in July 2022, when JWST used to be first starting its science operations. “[SN 1987A] was one of the first objects observed,” Fransson says, with JWST learning the supernova’s aftermath for approximately 10 hours.
“The only energy source capable of producing those [signs] is a neutron star,” says learn about co-author Patrick Kavanagh of Maynooth College in Eire. For a dark hollow to do the similar, it will wish to be ravenously feeding on subject from a supply—similar to any other megastar—for which there’s no proof. “We’re confident that we assessed all the different possibilities,” Kavanagh says. “We ruled out everything except the presence of a neutron star.”
Sparsely parsing the mild emitted through the ionized subject matter displays that the neutron megastar isn’t precisely on the center of SN 1987A; in lieu, it’s reasonably offset as it gained a “kick” from the supernova. Because the megastar exploded, any minor imbalances would have shifted extra of the outpouring subject to at least one facet or any other, inflicting the neutron megastar to draw back in the wrong way like an egg squeezed from a balloon. Observations recommend the neutron megastar is shifting reasonably towards us, having traveled about 500 billion kilometers from the web site of its cataclysmic start. “The kick velocity is around 400 kilometers a second,” Kavanagh says—unthinkably speedy for us right here on Earth however nonetheless glacially gradual towards the immensities of light-years.
What’s no longer sunny is whether or not SN 1987A’s remnant is simply a neutron megastar. In lieu it may well be a pulsar—a neutron megastar spinning so impulsively that it fires streams of power from its poles that sweep throughout a swath of sky like the beams of a cosmic lighthouse. “If there is a pulsar, the beam is not pointed at us, so we can’t detect it,” says Yvette Cendes of the Heart for Astrophysics | Harvard & Smithsonian, who used to be no longer concerned within the learn about. However there may well be in a different way to determine. In the usual neutron megastar state of affairs, the sheer warmth from the stellar remnant is so intense that it modes a beacon of ionized silicon this is scattered farther away within the increasing cloud. Within the pulsar type—the place emissions aren’t ruled through warmth however in lieu through winds of electrons and alternative debris that trauma the innermost particles—ionized silicon will have to be extra scarce. So if silicon can also be noticed and mapped round SN 1987A, “we can discern between the two,” Kavanagh says. As but unpublished follow-up JWST observations that had been taken through the workforce within the fall of 2023 and previous this era might include that resolution.
Those observations trade in brandnew insights into the earliest moments later a sort II supernova. “We haven’t seen the formation of a neutron star before,” Fransson says. Now that we have got, additional research of this cosmically younger object with JWST and alternative telescopes will have to permit astronomers to be informed a lot more about those bewildering stellar occasions. “Until we see a supernova in our own galaxy, this is the best studied one we’re going to have,” Cendes says.