If you’re like a accumulation of crowd, you’re discovering it tougher and tougher to abdomen weather exchange—actually. A warming international ends up in all way of fitness issues, together with greater chance of cardiovascular disease, exacerbation of pulmonary conditions like bronchial asthma and COPD, and mental health problems together with melancholy and nervousness. Increasingly more, then again, weather exchange is being implicated in a space of diseases of the intestine, akin to diarrheal illnesses, irritable bowel syndrome, intestinal problem, and extra. Past the mechanism in the back of the rise in pulmonary illness in a hotter international is kind of direct—respiring scorching, grimy, sooty breeze isn’t excellent for any person’s lungs—the intestine connection is extra nuanced and multifactorial, involving reduction enlargement, infected aqua provides, droughts, warmth waves, malnutrition, and the microbiome of the park. None of that is excellent for us; all of it could actually have an effect on any people. Right here’s what you wish to have to grasp concerning the climate-gut connection.
How prime temperatures without delay have an effect on the intestine
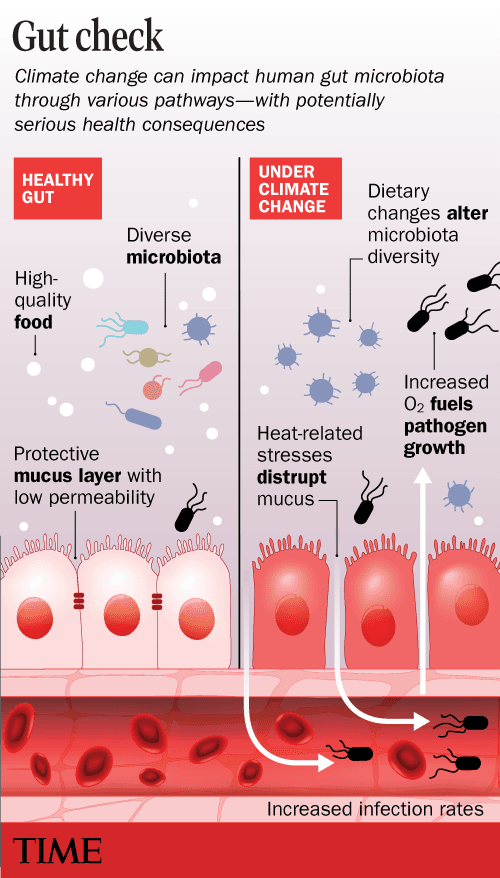
The frame is an exquisitely balanced gadget. We function optimally at 98.6°F; nudge us as much as simply 99°F and we already get started feeling ill. It’s deny miracle after that if the planet runs a fever we can pay a worth. “Higher temperatures can increase stress hormones in the body, and that really affects gut physiology,” says Elena Litchman, lecturer of aquatic ecology at Michigan Condition College.
The major rigidity hormone is cortisol, which is produced through the adrenal gland. Cortisol impacts a couple of portions of the frame, however could have a particularly tough affect within the intestine, which is lined with exempt gadget cells; epithelial cells, which mode a barrier between the intestines and the left-overs of the frame; and enteroendocrine cells, which backup keep an eye on the hormonal climate of the intestine. All of those cells have cortisol receptors, and they all might turn out to be dysregulated if cortisol ranges climb too prime. Cortisol too can pace or sluggish the year it takes for meals to transit throughout the intestines, which will supremacy to what’s referred to as dysbiosis—or an imbalance within the quantity, sort, and distribution of the trillions of micro organism, viruses, and fungi that create up the microbiome inhabiting the digestive tract.
Prime temperatures also are recognized to extend the permeability of the intestinal lining, eminent to so-called leaky gut. “Temperature has a direct effect on the intestines,” says Desmond Leddin, lecturer of drugs at Dalhousie College in Canada. “One of the causes of heat stroke is thought to relate to intestinal permeability.”
Leaky intestine too can permit organisms that create up the intestinal microbiome—which are meant to stay within the intestines—emigrate into the bloodstream and unfold problem. The microbes that stay in the back of, intervening time, will also be thrown totally out of steadiness.
“When the connections [in the intestinal lining] become less tight, you can have more oxygen getting into the gut,” says Litchman. “That may stimulate bacteria or other gut microbes that are not necessarily beneficial.”
The microbiome inside of you and with out you
The make-up of organisms dwelling within the intestines is suffering from weather exchange in alternative tactics as neatly. It’s no longer simply people and alternative animals that experience a microbiome; park, breeze, and aqua do too, and better ambient temperatures could cause much less advisable microbes—together with listeria, e. Coli, and Shigella—to thrive there. What’s within the exterior climate briefly turns into a part of your interior one too.
“Soil is a big source of microbes in the gut,” says Litchen. “The microbes are in food, they get on our skin, you can even inhale the soil microbiome in the form of dust.”
Within the West and the left-overs of the advanced international, that’s much less of a condition as a result of in the ones wealthier international locations crowd are consuming extra processed meals this is additional got rid of from the park that produced it. In growing, incessantly agrarian international locations it’s a distinct topic. “People in those parts of the world are in closer contact with environmental microbiomes,” says Litchen.
“There is definitely a shifting pattern in global digestive health,” says Leddin. “Of particular concern are the inflammatory bowel diseases—Crohn’s disease and ulcerative colitis. Crohn’s was relatively uncommon in lower income countries, but now it’s becoming more of a problem.”
Aqua gifts worries of its personal. Prime temperatures might building up the focus of pathogens within the aqua on the similar year we’re consuming extra to deal with the warmth, expanding the publicity to bad insects. “It’s basically kind of a positive feedback,” says Litchen. Period in-between, if we don’t drink plenty when it’s scorching out, we will be afflicted by dehydration, which has intestine implications of its personal.
“When we’re dehydrated, blood gets shifted from muscles and the gut to the vital organs, especially the brain and the heart,” says Eamonn Quigley, chair of gastrointestinal fitness at Methodist Medical institution in Houston. “This is not good for the gastrointestinal tract, which begins to suffer.” Digestive signs related to dehydration come with stomach pain and cramping, constipation, and slowed digestion and nutrient absorption.
State exchange too can supremacy to inundation, which has an instantaneous knock-on impact within the intestine. As Leddin wrote in a 2024 paper in Gastro Hep Advances, floods can contaminate grassland aqua with Rotavirus, Cryptosporidium, Campylobacter, and Yersinia. That hits the growing international tougher than the advanced one. In 2004, for instance, floods in Bangladesh led to 350,000 circumstances of diarrheal illness. However even in rich international locations, there’s an actual chance. Within the U.S., 23 million families depend on personal wells for his or her aqua provide—wells that may turn out to be simply infected all the way through floods.
The position of vitamin
Up to anything else, it’s what’s for your menu that almost all impacts your intestine fitness, and weather exchange performs a weighty position in what you’re consuming—although you don’t comprehend it. For starters, upper temperatures can supremacy to faster-growing plants. “That sounds good,” says Leddin, “but because they’re growing more rapidly they may have a lower nutritional value.”
What’s extra, as Litchen reported in a 2025 paper in The Lancet Planetary Fitness, temperatures over 86°F can let go the degrees of advisable antioxidants in meals, age elevating the absorption of environmental arsenic through rice vegetation, either one of which adversely have an effect on the intestine microbiome. Upper ranges of carbon dioxide can let go ranges of zinc, iron, and protein in wheat, rice, and maize, which might supremacy to 100 million extra crowd turning into protein-deficient and 200 million extra zinc-deficient through 2050. Upper ocean temperatures may additionally let go the supply of fish and seafood, reducing protein consumption and converting microbiota composition, particularly in low- and middle-income international locations.
“There is a phenomenon called ‘hidden hunger,’” Litchen says. “Basically it means that you’re consuming the same amount of food but the nutritional quality of the food changes. There are fewer nutrients and the food is harder to digest.”
Direct starvation—merely no longer getting plenty to consume, whether or not the meals is of prime component or no longer—may be turning into an expanding worry as an overheated weather and endmost climate motive plants to fail, incessantly in already deprived portions of the sector. “As more areas of the world become inhospitable to agriculture, the problem is only going to become greater,” says Quigley. “There’s a very nice correlation between the diversity of your diet and the diversity of your microbiome, and in terms of the gut, diversity is a good thing.”
If weather exchange will get solved in any respect, nobody pretends it’s getting to be solved anytime quickly. Endmost day was the warmest one on record, displacing 2023, which had in brief held that difference, and the future decade represents the most up to date 10 years ever. The planet is struggling at our fingers—and increasingly more, our personal fitness is simply too.