Setup of AAV capsid checking out in human liver
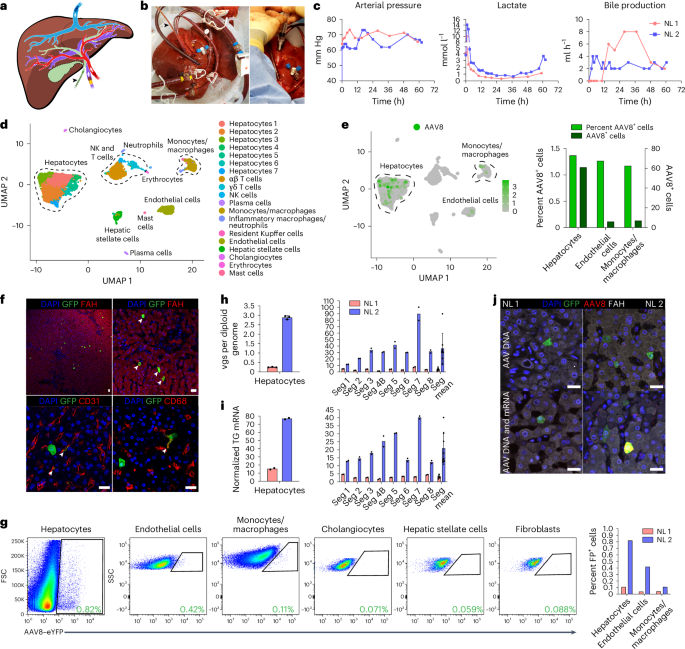
We first investigated the opportunity of long-term NMP with the commercially to be had OrganOx metra machine20 (past the 24 h worn clinically) the usage of a steatotic and fibrotic human liver (steatotic liver 1 (SL 1); Prolonged Knowledge Fig. 1a–c and Backup Desk 1). We changed 20% of the perfusate with PRBCs each and every 24 h or when the hemoglobin dropped to six g dl–1. We evaluated the perfused liver consistent with the similar standards worn clinically for deciding on transplantable livers by means of momentary NMP21. The liver used to be viable and purposeful for 103 h, as evidenced by means of lactate clearance (<2.5 mmol l–1), glucose metabolism (responsiveness to insulin) and pH (7.3–7.4), all deliberate within the perfusate, and bile manufacturing (>4 ml h–1; Prolonged Knowledge Fig. 1d). As well as, the liver remained attentive to steady infusion of a vasodilator by means of keeping up a strong hemodynamic profile (Prolonged Knowledge Fig. 1e).
To optimize long-term NMP, we added ordinary renal serve as by means of incorporating a hemoconcentrator into the NMP circuit, which we examined in any other steatotic liver (SL 2; Prolonged Knowledge Figs. 1a and 2a). Later 3 h of hemoconcentration, ranges of blood urea nitrogen, creatinine and osmolality within the perfusate have been lowered by means of about 20%, reflecting removing of misuse metabolites (Prolonged Knowledge Fig. 2b). We balanced electrolyte ranges by means of changing the hemofiltrate with isotonic dialysate (Prolonged Knowledge Fig. 2c).
We additionally worn perfusion of SL 2 to do away with biases from our option to AAV capsid analysis. We got rid of residual plasma, which will come with NAbs to AAV capsids27,28, by means of centrifugation-mediated ablution of PRBCs29, nearest which NAbs to the AAV2, AAV5, AAV6, AAV8 and AAV-DJ capsids become just about undetectable as assessed by means of luciferase-based neutralization assay (Prolonged Knowledge Fig. 3a). We additionally excluded lack of AAV vectors by means of attachment to the skin of the silicone tubing within the NMP circuit30 (Backup Fig. 1).
In the end, we minimized the era required to come across purposeful transduction, this is, mRNA and protein tonality by means of AAV vectors. We built a self-complementary AAV (scAAV) vector that expresses a fluorescent protein-encoding transgene from the cytomegalovirus (CMV) promoter. scAAV vectors specific transgenes extra swiftly than single-stranded AAV vectors as a result of they divergence the desire for second-strand DNA synthesis nearest uncoating of the viral particle within the nucleus31. The CMV promoter is ubiquitously lively, which permits for complete characterization of AAV capsid tropism32. Additionally, the CMV promoter supplies rapid-onset and high-level transgene tonality—it’s topic to silencing in hepatocytes however best nearest 7 days33. To spot the earliest era level when purposeful transduction might be reliably detected, we intravenously injected scAAV vectors produced with AAV8, AAV5, AAV-LK03 and AAV6 capsids into mice. Voice of vector-derived mRNA and fluorescent protein higher reasonably between 48 h and seven days nearest injection, reflecting ongoing purposeful transduction, however the relative transduction efficiencies of the 4 AAV vectors have been necessarily the similar between the 2 era issues (Backup Fig. 2a,b). Those effects led us to worth the scAAV-CMV vector for all next experiments (Backup Desk 2).
Those effects determine NMP as an experimental machine for checking out AAV capsids underneath physiological statuses in human livers and prohibit the important perfusion era nearest AAV vector management to 48 h.
Transduction profile of the AAV8 capsid in standard human liver
The use of our optimized way, we investigated the potency and specificity of hepatocyte transduction of a vector produced with the AAV8 capsid, which is maximum regularly worn in scientific trials of liver gene remedy1, in two human livers that have been histologically standard consistent with biopsies taken ahead of NMP (Backup Fig. 3 and Backup Desk 1). Perfusate bought ahead of vector infusion contained a tiny quantity of NAbs to the AAV8 capsid, confirming the efficacy of PRBC ablution (Prolonged Knowledge Fig. 3b). Later attaining an optimum hemodynamic and metabolic profile at 12 h of perfusion, we infused 5.7 × 1012 vector genomes (vgs) of AAV8–enhanced inexperienced fluorescent protein (AAV8–eGFP) into standard liver 1 (NL 1) and 1.6 × 1013 vgs of AAV8–enhanced yellow fluorescent protein (AAV8–eYFP) into NL 2 during the portal vein (Fig. 1a–c, Prolonged Knowledge Fig. 4a and Backup Desk 2). Those doses mirror the space given in scientific trials of liver gene remedy with AAV8 vectors3 however are calculated in keeping with liver weight in lieu of frame weight as a result of biodistribution isn’t a think about our machine (Backup Desk 1). We ascertained the capability of those AAV vectors nearest intravenous injection into mice (Prolonged Knowledge Fig. 5a). Declining vector DNA ranges within the perfusate indicated uptake into the liver (Backup Fig. 4a–c). We ended NMP when the lactate point started expanding to determine a physiological order (48 h nearest AAV infusion for NL 1 and 50 h for NL 2; Fig. 1c and Prolonged Knowledge Fig. 4a).
a, Caricature appearing cannulation of human liver and path of tide in blood vessels and the bile duct (gall bladder got rid of). b, Photographs of cannulated and perfused NL 1 (left) and AAV8–eYFP vector infusion into the portal vein (proper). Cannula colours are the similar in a and b, the place yellow signifies the portal vein, crimson signifies the hepatic artery, blue signifies the inferior vena cava, and the dark arrowhead signifies the bile duct. c, Viability and serve as deliberate throughout NMP of NL 1 and NL 2. Of word, in NL 2, infusion of one U of PRBCs at 60 h brought about an building up in lactate. In NL 1, bile manufacturing used to be now not recorded between 0 and 11 h because of a mispositioned bile duct cannula. d, Uniform manifold approximation and projection (UMAP) of 6,959 liver cells analyzed by means of scRNA-seq and clustered consistent with mobile identification; NK, herbal killer. e, Left, distribution of AAV8+ cells in scRNA-seq. Proper, proportion and absolute collection of AAV8+ cells in each and every mobile folk. f, Immunofluorescence for GFP (AAV8), FAH (hepatocytes), CD31 (endothelial cells) and CD68 (monocytes/macrophages) in tissue samples from NL 2 nearest NMP. White arrowheads point out cells confident for each GFP and the respective cell-type-specific marker; scale bars, 25 µm. g, Wave cytometry (left) with quantification (proper) of AAV8-transduced cells excused from NL 2 nearest 62 h of NMP; FP, fluorescent protein. h,i, Quantification of AAV vgs in step with diploid genome (h) and transgene (TG) mRNA tonality (i) in separate hepatocytes and tissue samples from NL 1 and NL 2. NL 1 gained 5.7 × 1012 vgs and NL 2 gained 1.6 × 1013 vgs. Values are introduced as cruel ± s.d. (n = 2 aside from n = 3 hepatocytes in h; technical replicates); Seg, section; Seg cruel, cruel tonality values of all 8 sections. j, ISH of AAV vector DNA the usage of an eGFP sense probe (manage) and each AAV vector DNA and mRNA the usage of an eGFP antisense probe (base) blended with immunofluorescence for GFP in tissue samples from NL 1 and NL 2; scale bars, 25 µm.
Later NMP ended, we enzymatically excused hepatocytes and nonparenchymal cells (NPCs), together with endothelial cells, monocytes/macrophages, cholangiocytes and mesenchymal cells (hepatic stellate cells and fibroblasts), and analyzed them by means of single-cell RNA sequencing (scRNA-seq). Research of 6,959 cells from NL 2 confirmed 6 most important and 14 particular mobile varieties (Fig. 1d and Backup Fig. 5a–e), with hepatocytes being maximum successfully transduced by means of the AAV8 vector, carefully adopted by means of endothelial cells and monocytes/macrophages (Fig. 1e). Immunostaining of fluorescent protein-expressing cells in tissue divisions and tide cytometry with optimized antibody panels (Prolonged Knowledge Fig. 6a–d) showed the AAV8 capsid tropism known by means of scRNA-seq self reliant of vector dose (Fig. 1f,g). Quantitative virtual droplet PCR (ddPCR) confirmed dose-dependent variations in vector DNA and transgene mRNA in separate hepatocytes and tissue samples of the 8 liver sections from the 2 livers, with tight correlation between the 2 parameters (Fig. 1h,i). In situ hybridization (ISH) with sense or antisense probes concentrated on vector DNA or each vector DNA and transgene mRNA showed this outcome (Fig. 1j).
Those effects display that the tropism of the AAV8 capsid within the standard human liver comprises endothelial cells and monocytes/macrophages along with hepatocytes. Those effects additionally determine that the AAV8 capsid gives environment friendly purposeful transduction within the human liver as evidenced by means of corresponding ranges of bodily vector mobile access and transgene tonality, with scRNA-seq being similarly as informative as tide cytometry.
Comparability of AAV capsids in standard and steatotic human livers
We when compared the transduction profile of the AAV8 capsid with that of the AAV5, AAV-LK03 and AAV6 capsids, which can be maximum regularly worn in scientific trials of liver gene remedy1, and the AAV-NP59 capsid, which, in keeping with research in immune-deficient mice, has the most powerful tropism for human hepatocytes34. To facilitate side-by-side comparability, for each and every capsid, we presented a novel fluorescent protein-encoding transgene and expressed barcode into the AAV vector, making an allowance for difference by means of tide cytometry, microscopy and ddPCR (Backup Fig. 6a–d and Backup Desk 2). We ascertained that scRNA-seq reliably detects transgenes and barcodes (see Methods) and excluded that co-injection of AAV vectors produced with the other capsids alters the transduction potency of anyone capsid in mice (Backup Fig. 6e,f).
Ahead of checking out in human liver, we intravenously co-injected the AAV vectors on the similar dose into wild-type mice and FRGN mice repopulated with human hepatocytes. Two days next, we enzymatically excused hepatocytes and analyzed fluorescent protein tonality by means of tide cytometry. We discovered a capsid-specific transduction potency of AAV8 > AAV6 > AAV5 > AAV-LK03 > AAV-NP59 in mouse hepatocytes and AAV-NP59 > AAV-LK03 > AAV8 > AAV6 > AAV5 in human hepatocytes (Prolonged Knowledge Fig. 5b–h), which is in contract with stories of species-specific hepatocyte tropism of those capsids10,11,12,13,34.
Since the anticoagulant heparin worn for NMP within the scientific atmosphere can shed the transduction potency of the AAV-LK03, AAV6 and AAV-NP59 capsids35,36, we substituted low-molecular-weight heparin nearest screening extra anticoagulants in mice (Backup Fig. 7a–c).
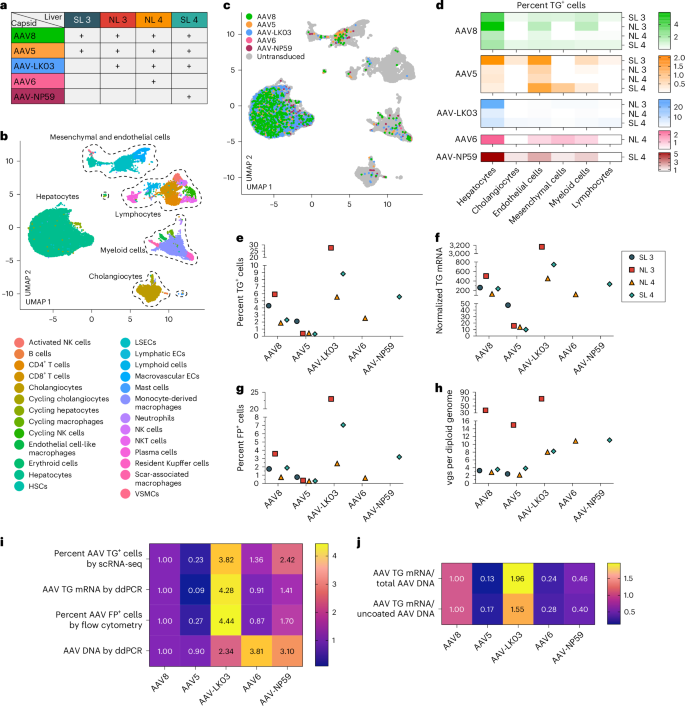
We co-infused AAV vectors produced with the 5 capsids into 4 human livers, two histologically standard (NL 3 and NL 4) and two steatotic (SL 3 and SL 4; Backup Fig. 3 and Backup Desk 1). To contextualize our effects, we sequentially presented extra AAV vectors together with AAV8, which served as an inner keep watch over, with the AAV8, AAV5, AAV-LK03, AAV6 and AAV-NP59 capsids being examined in 4, 4, 3, one and one livers, respectively (Fig. 2a). We co-infused AAV vectors on the similar dose, starting from 6.7 × 1011 vgs to a few.4 × 1013 vgs in step with vector between livers (Backup Desk 2). Each standard and steatotic livers have been viable, as assessed by means of research of liver shock and serve as in perfusate and mobile loss of life in tissue divisions, and hemodynamically strong all through NMP, as much as and together with the termination era of 60–73 h nearest AAV vector infusion (Prolonged Knowledge Fig. 4a,b). We retrieved hepatocytes and NPCs at lofty submit from all livers, making an allowance for built-in clustering of 6 most important and 26 particular mobile varieties by means of scRNA-seq (Fig. 2b and Backup Fig. 8a). All 5 AAV vectors basically transduced hepatocytes. Amongst NPCs, endothelial cells and myeloid cells have been maximum steadily transduced, while cholangiocytes, mesenchymal cells and lymphocytes confirmed low ranges of transduction (Fig. 2c,d). Particularly, AAV-LK03 used to be maximum particular for hepatocytes, with minimum transduction happening in NPCs.
a, Assignments of AAV capsids to human livers for side-by-side comparability. SL 3 gained 3.4 × 1013 vgs, NL 3 gained 5.5 × 1012 vgs, NL 4 gained 6.7 × 1011 vgs and SL 4 gained 3.0 × 1012 vgs of each and every vector. Of word, the low-producing AAV6 capsid dictated the decrease dose in NL 4. b, UMAP of 35,807 cells from 4 livers analyzed by means of scRNA-seq and clustered consistent with mobile identification; ECs, endothelial cells; LSECs, liver sinusoidal endothelial cells; HSCs, hepatic stellate cells; VSMCs, vascular clean muscle cells. c, UMAP appearing cells transduced by means of AAV capsids. d, Warmth map appearing p.c transduction by means of AAV capsids throughout mobile populations. e,f, Quantification of AAV transgene mRNA-expressing hepatocytes by means of scRNA-seq (e) and ddPCR (f). g, Quantification of AAV fluorescent protein-expressing hepatocytes by means of tide cytometry. h, Quantification of AAV vector DNA (vgs) in step with diploid genome in hepatocytes by means of ddPCR. i, Warmth map appearing the relative ranges of AAV vector mRNA, protein and DNA amongst 5 AAV capsids normalized to the degrees of AAV8. The degrees from 4 livers have been averaged for each and every capsid. j, Warmth map appearing the relative ranges of the ratio between AAV transgene mRNA and general AAV vector DNA from hepatocytes (manage row) and AAV transgene mRNA and uncoated nuclear AAV vector DNA from tissue samples (base row). Ranges have been normalized to the degrees of AAV8 and averaged from 4 livers for each and every capsid.
We nearest quantified capsid-specific transduction on the mRNA, protein and DNA ranges in hepatocytes by means of scRNA-seq, tide cytometry and ddPCR. In hepatocytes, we discovered a purposeful transduction (mRNA and protein) potency of AAV-LK03 > AAV-NP59 > AAV8 ≥ AAV6 > AAV5 (mRNA space: 27.7% to 0.3%, protein space: 23% to 0.3%) and a bodily transduction (DNA) potency of AAV6 > AAV-NP59 > AAV-LK03 > AAV8 > AAV5 (space: 70.9 to two.2 vgs in step with diploid genome; Fig. 2e–i and Backup Fig. 9a–d). The relative transduction potency within the 8 sections of each and every liver paralleled the degrees in hepatocytes, which we showed in tissue divisions by means of ISH of vector DNA and mRNA (Backup Figs. 10a–c and 11a–d). Detection of distinctive capsid barcode sequences isolated by means of scRNA-seq additional showed the capsid transduction hierarchy (Backup Fig. 10d). Particularly, the purposeful transduction potency of AAV-NP59 used to be 55% lower than that of AAV-LK03, the other of what has been reported in immune-deficient mice engrafted with human hepatocytes, which we independently showed34 (Prolonged Knowledge Fig. 5e,f,h).
We additionally investigated capsid-specific variations in transcription potency by means of quantifying the ratio of AAV transgene mRNA to uncoated AAV vgs inside nuclei, this is, DNA to be had for transcription (Backup Fig. 10e–g). Transcription potency used to be easiest for AAV-LK03 and lowest for AAV5 (Fig. 2j).
Those effects display that the AAV-LK03 capsid transduces hepatocytes in human liver a lot more successfully and particularly than the AAV-NP59, AAV8, AAV6 and AAV5 capsids. By way of forming the prevalence of AAV-LK03 for hepatocyte-targeted human liver gene remedy, our effects spotlight barriers of immune-deficient mice engrafted with human hepatocytes34. As well as, those effects discover capsid-specific results on AAV vector transcription within the human liver, which aligns with stories of an epigenetic position of the AAV capsid37,38.
AAV capsid-specific results of hepatocyte zonation and steatosis
To resolve whether or not any of the 5 AAV capsids preferentially transduces hepatocytes in a selected zone of the human liver and the way this tropism is also altered within the atmosphere of steatosis, we analyzed scRNA-seq knowledge from 22,146 hepatocytes from NL 3, NL 4, SL 3 and SL 4. We generated a periportal and pericentral ranking derived from the tonality of zonation markers conserved throughout all 4 livers to quantify the zonation enrichment on a in step with mobile foundation (Prolonged Knowledge Desk 1), which open a constant trend of purposeful zonation without reference to weakness order (Fig. 3a and Prolonged Knowledge Fig. 7a). In a similar fashion, in assessing the impact of steatosis on those parameters, we followed a nonbinary option to mobile classification by means of scoring each and every mobile in my opinion in keeping with tonality of steatotic marker genes (Fig. 3a and Prolonged Knowledge Desk 1). This way open a spectrum of steatosis, with standard livers containing some steatotic cells and steatotic livers containing some standard cells, and enabled us to spot CXCL8 as a extremely particular and conserved marker of steatotic hepatocytes throughout standard and steatotic livers (Prolonged Knowledge Desk 1 and Prolonged Knowledge Fig. 7b).
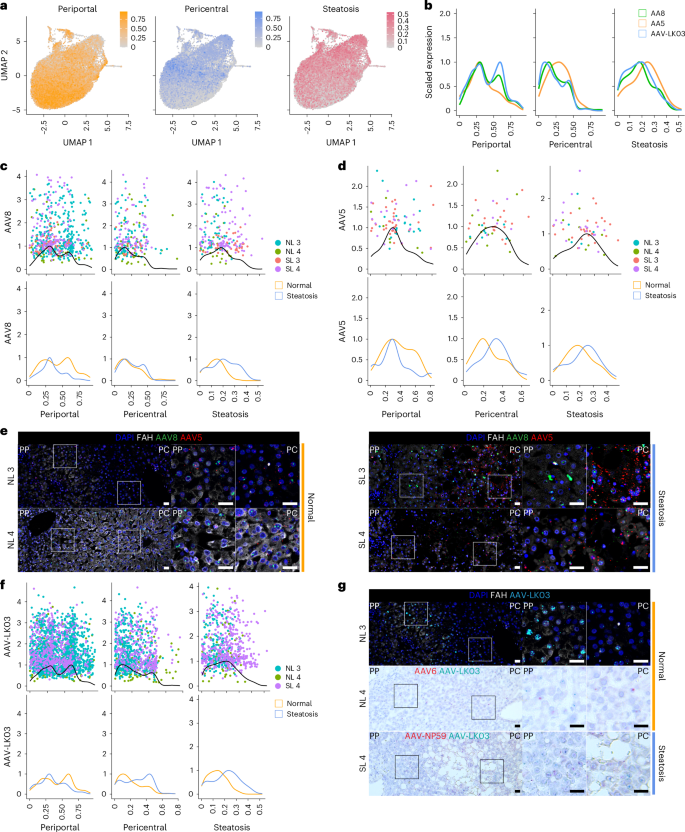
a, Gene module ratings for periportal and pericentral zonation and steatosis implemented to UMAPs of twenty-two,146 hepatocytes from 4 livers analyzed by means of scRNA-seq. b, Kernel density estimation histograms of transgene-positive hepatocyte distribution throughout gene module ratings. c, Kernel density estimation histograms of hepatocytes transduced by means of the AAV8 capsid throughout gene module ratings (manage) and separated by means of weakness order (base). d, Kernel density estimation histograms of hepatocytes transduced by means of the AAV5 capsid throughout gene module ratings (manage) and separated by means of weakness order (base). e, ISH of AAV8 and AAV5 vector DNA with sense probes in tissue samples; scale bars, 25 µm; PP, periportal; PC, pericentral. f, Kernel density estimation histograms of hepatocytes transduced by means of the AAV-LK03 capsid throughout gene module ratings (manage) and separated by means of weakness order (base). g, ISH of AAV-LK03 vector DNA with sense probes in tissue samples. Kernel density estimation histograms for AAV6 and AAV-NP59 capsids are proven in Prolonged Knowledge Fig. 7f; scale bars, 25 µm.
We additionally investigated whether or not probably the most steatotic hepatocytes showcase altered transcriptomic signatures. We considering hepatocytes from SL 4, probably the most steatotic liver by means of histologic ranking, as a result of 42% of those hepatocytes clustered one after the other from the alternative livers regardless of integration (Prolonged Knowledge Fig. 7c). Those clusters have been uniquely enriched for tonality of genes within the NADPH relief pathway (TXNRD1, GCLM, AKR1C1 and AKR1C2), which performs an notable position in fatty acid biosynthesis39 (Prolonged Knowledge Fig. 7d,e). Zonation used to be retained in those cells, in keeping with it being altered best in end-stage liver weakness40 (Fig. 3a and Prolonged Knowledge Fig. 7a).
Those effects confirmed that our steatosis scoring form as it should be displays tissue histology and that our zonation scoring form is acceptable to all livers irrespective of steatosis severity. We implemented those forms to resolve the consequences of steatosis on AAV capsid transduction at single-cell solution. We first when compared AAV capsid conduct by means of plotting hepatocytes transduced with the 3 capsids maximum regularly worn in scientific trials towards their respective zonation and steatosis ratings (Methods and Fig. 3b). This research open upper periportal ratings for AAV8 and AAV-LK03 than for AAV5, which conversely confirmed distinctive pericentral ranking enrichment. AAV5 transduction used to be related to a better steatosis ranking, which mirrored its lofty pericentral ranking41 (Fig. 3b).
Nearest, we analyzed standard and steatotic livers one after the other to resolve the contribution of weakness order to zonation of AAV capsid transduction. Our scoring form confirmed that the vulnerable periportal zonation of AAV8 used to be particular to standard livers (Fig. 3c), while pericentral zonation of AAV5 used to be particular to steatotic livers (Fig. 3d), which we showed in tissue divisions by means of ISH of vector DNA (Fig. 3e) and/or mRNA (Backup Fig. 11a–d). We discovered differential tonality of genes related to steatosis and steatotic liver weakness in hepatocytes solely transduced by means of AAV5. Pericentrally zonated LPCAT2 (ref. 42) and LPCAT1, genes occupied with phosphatidylcholine biosynthesis and lipid droplet formation and reworking43, have been enriched, while FADS1, which protects hepatocytes from lipid bundle44, and FADS2 have been depleted in SL 3; C3AR1 and DUSP9, which control lipid bundle45,46, have been enriched in SL 4, and pericentrally zonated SLCO1B3 (ref. 47) used to be enriched in each steatotic livers (Backup Knowledge 1). ISH showed that AAV5 favors steatotic pericentral hepatocytes by means of appearing vector DNA (Fig. 3e) and/or mRNA (Backup Fig. 11a,d) collecting in lipid-laden cells. There have been additionally steatosis-dependent adjustments in AAV-LK03 zonation. The robust periportal zonation of AAV-LK03 seen in standard liver used to be misplaced within the atmosphere of steatosis, the place its pericentral zonation used to be higher, which we showed by means of ISH of tissue divisions (Fig. 3f,g and Backup Fig. 11b–d). For AAV6, our zonation type and ISH confirmed vulnerable periportal zonation in standard liver, while AAV-NP59 confirmed pericentral zonation in steatotic liver (Prolonged Knowledge Fig. 7f and Backup Fig. 11c,d). Those tropisms may just now not be defined by means of the presence or a lack of identified AAV access components48 (Backup Fig. 8b,c). A lofty steatosis ranking didn’t negatively have an effect on the transduction potency of any of the AAV capsids we examined (Fig. 3c,d,f).
Particularly, we known a folk of nonzonated hepatocytes each in standard and steatotic livers marked by means of the tonality of SOX9, SPP1 and TACSTD2 (Prolonged Knowledge Fig. 7g–i). The collection of TACSTD2 (TROP2)-expressing hepatocytes higher significantly with steatosis severity, which used to be now not paralleled by means of an building up in markers of proliferation (Prolonged Knowledge Fig. 7j,k), suggesting that TROP2 tonality in hepatocytes displays response to weakness, now not growth of a progenitor mobile folk as up to now instructed19. The cells may also be transduced by means of all capsids we examined, with AAV-LK03 being the most productive, which highlights this hepatocyte folk as a possible healing goal in steatotic liver weakness (Prolonged Knowledge Fig. 7l).
Those effects display that the AAV-LK03 capsid preferentially transduces periportal hepatocytes in standard human liver however lacks this zone-specific tropism within the steatotic human liver. AAV8 presentations homogeneous tendencies, however its periportal hepatocyte tropism is way much less pronounced in human liver than in NHP liver16. In the meantime, the AAV5 capsid has a powerful tropism for pericentral hepatocytes within the steatotic human liver however transduces hepatocytes calmly within the standard human liver49.
AAV capsid-specific and steatosis results on vector episome formation
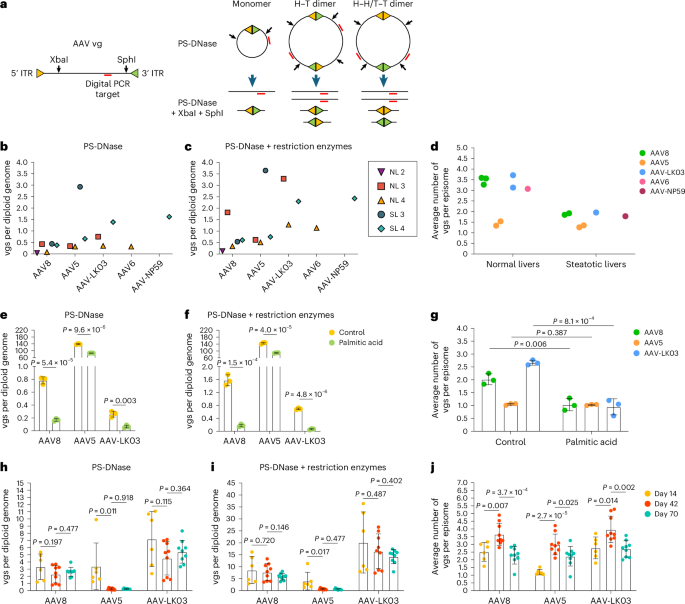
We nearest investigated whether or not steatosis affects episome formation of AAV vectors, which is significant for long-term transgene tonality50. We separate nuclei from liver tissue from NL 2, NL 3, NL 4, SL 3 and SL 4 to quantify vector episomes the usage of virtual PCR (Fig. 4a and Methods)49 and showed that round monomers and concatemers method in human livers inside 73 h (Fig. 4b,c). We discovered fewer vgs in episomes separate from steatotic livers than in episomes separate from standard livers, self reliant of which of the 5 AAV capsids used to be worn to make the vector, suggesting that round concatemerization of AAV vectors used to be compromised in steatotic livers (Fig. 4d).
a, Schematics appearing predicted AAV vg constructions following remedy with Plasmid-Shield DNase (PS-DNase) isolated or together with restriction enzymes (XbaI and SphI). PS-DNase remedy permits for quantification of round episomes by means of virtual PCR; extra restriction enzyme remedy permits for quantification of general vector DNA (vgs) in round episomes; H–T, head to tail; H–H, face to face; T–T, tail to tail. b,c, Quantification of round episomes (b) and general vgs in round episomes (c) in nuclei from section 3 of human liver tissues. BmtI and SphI have been worn to snip vector DNA from SL 3. d, Quantification of the typical collection of vgs in step with episome in nuclei from section 3 of standard livers (NL 2, NL 3 and NL 4) and steatotic livers (SL 3 and SL 4). The common quantity used to be calculated by means of dividing the quantity in c by means of the quantity in b. e–g, Quantification of round episomes (e), general vgs in round episomes (f) and the typical collection of vgs in step with episome (g) in general DNA from iPS cell-Heps 7 days nearest AAV vector transduction. 3 AAV vectors have been cotransduced at multiplicities of problem of 20,000 for the AAV8 capsid, 1,000 for the AAV5 capsid and 30 for the AAV-LK03 capsid. Palmitic acid used to be added at 200 µM each and every 2 days for 9 days. Values are introduced as cruel ± s.d. (n = 3, technical replicates). h–j, Quantification of round episomes (h), general vgs in round episomes (i) and the typical collection of vgs in step with episome (j) in tissue samples from FRGN mouse livers repopulated with human hepatocytes nearest co-injection of AAV vectors on the similar dose of four × 1010 vgs. Values are introduced as cruel ± s.d. (six lobes from two mice at future 14, 9 lobes from 3 mice at future 42 and 9 lobes from 3 mice at future 70; organic replicates). Way have been when compared the usage of two-tailed unpaired t-tests.
To substantiate this outcome, we analyzed episome formation by means of vectors produced with the AAV8, AAV5 and AAV-LK03 capsids cotransduced into human precipitated pluripotent stem cell-derived hepatocytes (iPS cell-Heps) handled with palmitic acid, a saturated fatty acid that reasons steatosis51. As a prerequisite, we ascertained that cotransduction does now not have an effect on quantification of episome formation (Prolonged Knowledge Fig. 8a–c). We discovered that palmitic acid remedy for 7 days brought about the collection of episomes to say no (Fig. 4e,f). Palmitic acid had minute impact on bodily transduction and transgene tonality, indicating that now not best episomes but additionally unbending vectors are to be had for transcription quickly nearest transduction (Prolonged Knowledge Fig. 8d,e). Confirming our findings in human livers, AAV8 and AAV-LK03 vectors did not method concatemers in steatotic iPS cell-Heps, while the AAV5 vector used to be unaffected as it predominantly shaped round monomers regardless of a lofty collection of transduced vgs (Fig. 4g and Prolonged Knowledge Fig. 8d).
Nearest, we investigated long-term episome formation by means of AAV vectors, that specialize in the unique impact of the AAV5 capsid, prominent to primary formation of round monomers in human livers (Fig. 4b–d and Prolonged Knowledge Fig. 8f). We analyzed AAV8, AAV5 and AAV-LK03 episomes in FRGN mice repopulated with human hepatocytes to greater than 90% (ref. 52). The collection of vgs in AAV8 and AAV-LK03 episomes used to be strong for 70 days, and so they swiftly shaped immense concatemers (Fig. 4h–j). This discovering confirms findings in livers of NHPs the place concatemers shaped as early as 3 days and lasted for 90 days nearest intravenous injection of an AAV8 vector53. Against this, the collection of vgs in AAV5 episomes declined over era, almost definitely as a result of abasement, with concatemers being observable best by means of future 42. The collection of vgs in episomes dictated the transcriptional output in any respect era issues for all capsids, with unbending vgs almost definitely contributing to transcription to begin with (Prolonged Knowledge Fig. 8g,h). AAV5 episomes had the bottom transcription potency throughout all era issues, contradicting earlier findings in mouse liver that monomers are extra successfully transcribed than concatemers54. Episome kinetics of those capsids have been homogeneous in wild-type mice, with AAV5 appearing fast round monomer formation adopted by means of a steep abatement within the collection of vgs in episomes and concatemerization happening best by means of future 40 (Prolonged Knowledge Fig. 8i–l).
Those effects disclose that the AAV capsid influences the kinetics of vector episome formation, almost definitely by means of affecting the recombination of inverted terminal repeats (ITRs)55. The AAV5 capsid reasons formation of quite distracted episomes that concatemerize extra slowly than AAV8 and AAV-LK03 episomes, which interprets into decrease long-term transgene tonality. As well as, those effects determine steatosis as a capsid-independent issue impairing episome concatemerization and thereby the sturdiness of transgene tonality from AAV vectors.
AAV capsid-specific nonhepatocyte tropism and co-regulated genes
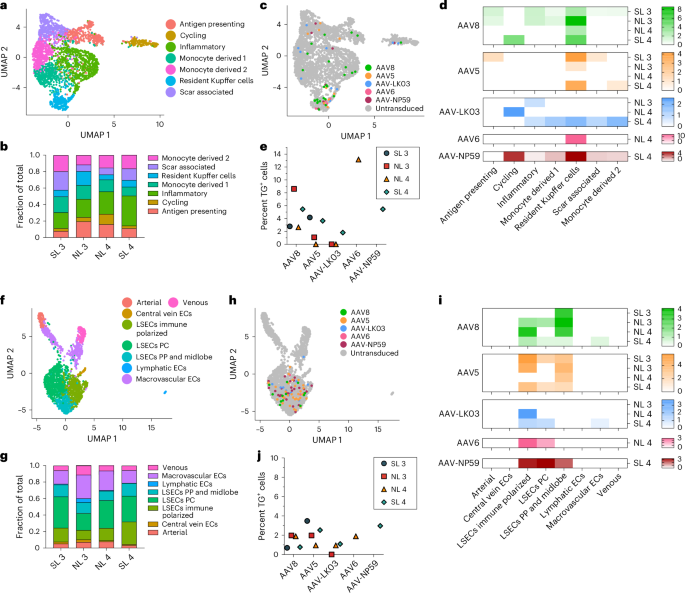
The tropism of AAV capsids for human liver mobile varieties past hepatocytes is unknown, which will have contributed to headaches or obscured alternatives within the scientific atmosphere. Our built-in dataset from NL 3, NL 4, SL 3 and SL 4, together with over 35,800 cells and 26 particular mobile varieties, open that AAV vectors persistently transduce now not best hepatocytes but additionally endothelial cells and monocytes/macrophages (Fig. 2c,d). We one after the other analyzed all endothelial cells and monocytes/macrophages to spot possible heterogeneity in transduction inside those populations. From 2,759 monocytes/macrophages, we discerned seven distinct varieties, together with scar-associated macrophages reported in fibrotic livers56 that have been maximum popular in SL 3 and SL 4 (Fig. 5a,b and Prolonged Knowledge Fig. 9a). We discovered a sunlit tropism for resident Kupffer cells of all capsids aside from AAV-LK03, with AAV6 and AAV8 being best, transducing as much as 13.2% and eight.6% of Kupffer cells, respectively (Fig. 5b–e).
a, UMAP of two,759 monocytes/macrophages from 4 livers clustered consistent with mobile subtype. b, Crowd distribution of monocyte/macrophage subtypes. c, AAV-transduced cells visualized by means of UMAP. d, Warmth map appearing p.c transduction by means of AAV capsids of monocyte/macrophage subtypes. e, Quantification of AAV transgene mRNA-expressing Kupffer cells by means of scRNA-seq. f, UMAP of two,091 endothelial cells from 4 livers clustered consistent with mobile subtype; ECs, endothelial cells; LSECs, liver sinusoidal endothelial cells; PP, periportal; PC, pericentral. g, Crowd distribution of endothelial mobile subtypes. h, AAV-transduced cells visualized by means of UMAP. i, Warmth map appearing p.c transduction by means of AAV capsids of endothelial mobile subtypes. j, Quantification of AAV transgene mRNA-expressing LSECs by means of scRNA-seq.
Subclustering of two,091 endothelial cells prominent 8 subpopulations, of which the 5 capsids nearly solely transduced liver sinusoidal endothelial cells (LSECs), with AAV5 and AAV8 being best (Fig. 5f–j and Prolonged Knowledge Fig. 9b). In steatotic livers, AAV5 transduced LSECs 3.3–5 instances higher than AAV8 to a most of three.5%, while in standard livers, AAV8 used to be identical or higher than AAV5 at 2% (Fig. 5j and Prolonged Knowledge Fig. 9c). This distinctive tropism almost definitely displays the rise in immune-polarized LSECs in steatotic livers, that have been transduced extra spontaneously by means of AAV5 (Fig. 5g,i). Those effects indicated that, as with hepatocytes, the steatotic state will increase the transduction of LSECs by means of AAV5. As well as, those effects highlighted LSECs (the physiological supply of issue VIII and von Willebrand issue) as an extra and extra physiologically related goal than hepatocytes for hemophilia A57 or von Willebrand weakness gene remedy58,59. In aid of this perception, the transduction potency of LSEC subtypes by means of the AAV8 and AAV5 capsids approached or surpassed ranges present in hepatocytes transduced with the similar capsids (Figs. 2d and 5i). Additionally, 1.25% of general LSECs expressed MKI67 or TOP2A, which is similar to the 1.30% of hepatocytes discovered to specific those markers and suggests a homogeneous handover charge and thus AAV vector patience between the 2 mobile varieties60 (Prolonged Knowledge Fig. 9d).
In the end, we wished to outline possible host components occupied with or suffering from transduction of the 5 AAV capsids in hepatocytes from NL 3, NL 4, SL 3 and SL 4 (Backup Knowledge 1). We discovered deny proof for activation of inflammatory signaling by means of AAV vectors in hepatocytes (Backup Fig. 8d). Differential gene tonality research of three,749 hepatocytes uniquely transduced with one of the most 5 AAV vectors additional confirmed that almost all upregulated genes showcase a negligible building up in tonality (wood2 (line trade) < 1), indicating that AAV vectors don’t perturb the host mobile transcriptome (Backup Knowledge 1). That specialize in considerably coenriched genes familiar to a minimum of 3 capsids highlighted PIGR, which regulates the transcytosis of released complexes for protecting towards viral problem61, and APOC1, a cofactor mediating hepatitis C virus problem62. CSH2 used to be probably the most considerably coenriched gene in hepatocytes transduced with the AAV8, AAV-LK03 or AAV-NP59 capsid in NL 2, NL 3 and SL 4 (Backup Knowledge 1 and Backup Fig. 12a,b). Regardless of proof that CSH2 performs a task in regulating hepatitis B virus transcription63 or within the virus protection reaction64, its position in AAV vector transduction is unknown.
Those effects outline the human NPC tropism of the 4 AAV capsids maximum regularly worn in scientific trials of liver gene remedy1 and a promising fresh capsid engineered to particularly transduce human hepatocytes34. Illustrating the price of those effects, they recommend LSECs as a physiological goal for gene remedy of hemophilia A or von Willebrand weakness the usage of the AAV5 or AAV8 capsid. Those effects additionally spotlight capsid-specific genes probably occupied with AAV trafficking or transcription and display transcriptomic balance of hepatocytes transduced with AAV vectors.